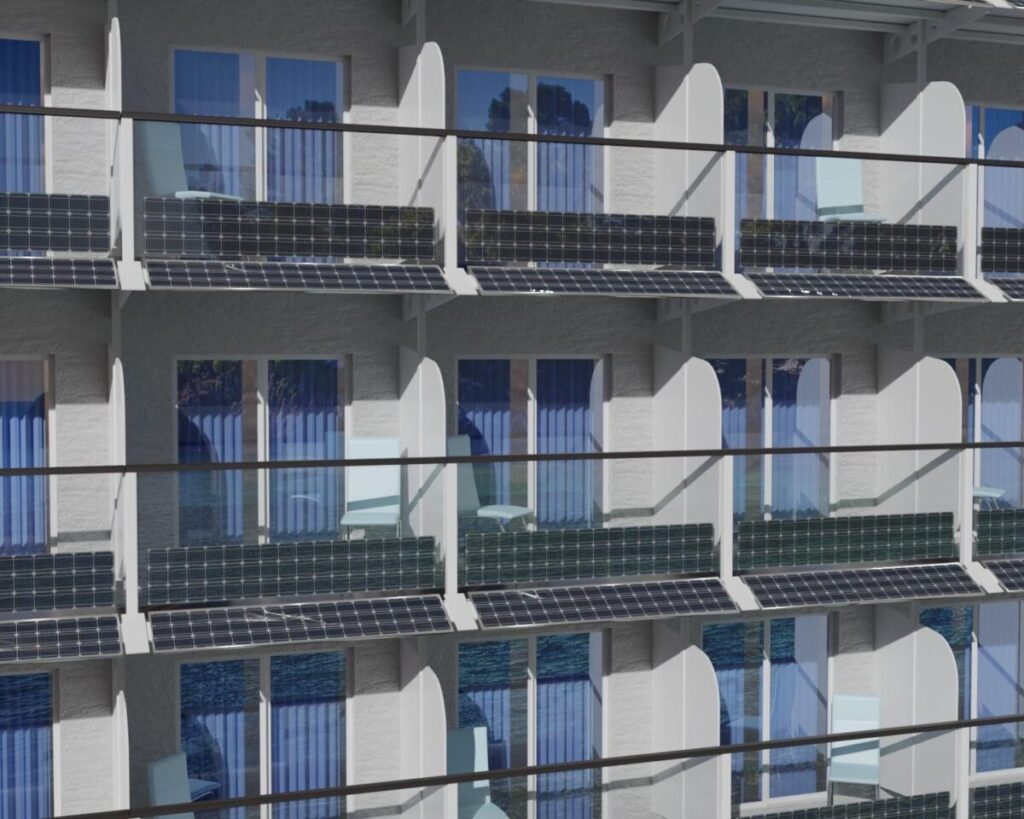
Scientists have simulated the delivery of PV modules to the balconies of cruise ship cabins. They tested the systems with three DC configurations and simulated them while cruising in the Caribbean and along the Norwegian and Danish coasts.
A research group led by scientists from the German Aerospace Center (DLR) has simulated the delivery of PV modules to cruise ship cabins to power their utilities.
As the cruise industry moves to Direct Current (DC) built-in grids, the team has proposed three approaches to PV integration, comparing them for efficiency. To find the ideal approach, they simulated cruises in the Caribbean and along the Norwegian and Danish coasts and presented the system’s performance.
“This paper presents a realistic photovoltaic system for a cruise ship, with potential for optimization. Furthermore, it proposes a subdivision of the PV system and on the voltage level at which it can be connected,” they said. “The concept will be further developed with the introduction of a battery storage system specifically designed for this application area. This system adopts both system serving and safety related tasks. ”
In their proposal, two 250 W and 22% efficient panels are installed on each cabin balcony—one is integrated into the balcony’s glass barrier at an angle of 90◦; The other is installed at an angle of 30◦, under the balcony and between the decks. For scale, a Helios Class cruise ship has 1,655 balcony cabins and would therefore have a maximum output of 827.5 kW.
Image: DLR Institute of Networked Energy Systems, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, CC by 4.0
“The assumed DC DC distribution grid is based on two voltage levels, 700 V and 350 V. The 700 V grid, starting from the engine room, is considered the main low voltage distribution and provides power to all fire zones on the ship,” the academics explained. “A fire zone is defined as an area that can be isolated from other areas by means of automatic fire barriers. The power distribution for each deck in a firing zone, consisting of nine starboard, nine port and 18 interior cabins, is unidirectional and has a lower voltage level of 350 V. The cabins are powered by a 48 V network, which is supplied from the 350 V – distribution network. ”
Based on those characteristics, the group has suggested three designs: in the first, the solar modules are directly connected to the 48 V cabin grid; In the second they are connected to the 350 V distribution network; And in the latter they are linked to the primary 700 V grid. By comparing all proposals, the team found that the third design has a conversion loss of 2% to 3% greater than the other two systems. The cabin grid suggestion was the safest, but also with the highest cost and maintenance effort. Since the 350 V distribution network was safer than the 700 V grid proposal and cheaper and with less maintenance than the cabin room system, it was chosen as the ideal one for the simulation task.
A series of simulations were performed to determine the optimal battery size and only one deck of a fire zone was considered for the simulation.
“The battery is used to provide emergency power and to buffer peak loads in the 36 cabins during normal operation,” the team said. “Given that 18 interior cabins have to be supplied by the PV systems of the 18 external cabins, it cannot be assumed that the energy output will be sufficient. It is therefore essential to connect to the 700 V grid. Consequently, the battery must be of sufficient size to ensure a constant flow of energy from 700 V to the 350 V grid.”
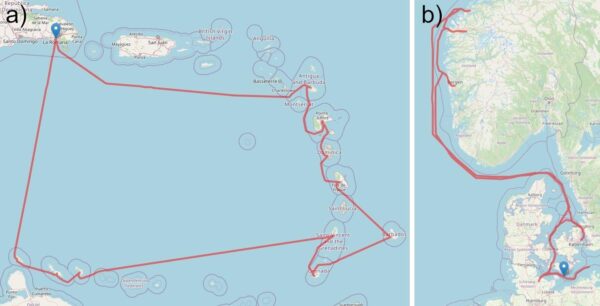
Image: DLR Institute of Networked Energy Systems, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, CC by 4.0
The deck simulation was worn on a 15-day Caribbean cruise that took place in March and on an 8-day cruise off the coast of Denmark and Norway that took place from August to September. One hundred simulations were performed using Python; In each, 37 demand profiles were randomly assigned to each cabin. It was assumed that a lithium iron phosphate (LIFEPO4) battery would ensure safe operation on deck.
“The observed self-sufficiency levels of 45% for the Caribbean cruise and 47% for the Norwegian cruise indicate significant potential for energy savings. If these values are extrapolated to an entire Helios class ship, an average of 3.2 MWh and 3.8 MWh respectively can be saved,” the research team said. “To maintain a continuous auxiliary supply of the on-board electrical system, 1.8 kW in the Caribbean and 2 kW in the Norwegian case is required. To ensure safe operation, a battery capacity of 161.4 AH is required for the Caribbean cruise and 127.5 AH for the Norwegian cruise. ”
Their findings were presented in “Efficiency analysis and performance modeling of a photovoltaic system for cruise ship cabins with battery storage using direct current distribution networks‘Published in the International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems. Scientists from Germany’s DLR Institute of Networked Energy Systems and Siemens Energy Global conducted the research.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you would like to collaborate with us and reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content


