Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have identified a high-energy, high-performance hybrid sodium-ion battery that can be charged in just seconds. The system integrates anode materials typically used in batteries with cathodes suitable for supercapacitors.
Sodium-ion energy storage systems have received considerable attention due to their superior safety, raw material costs, and environmental performance compared to ubiquitous lithium-ion batteries. However, the technology is unlikely to challenge the incumbent until costs are reduced by improving technical performance, establishing supply chains and achieving economies of scale.
There are two types of sodium-ion energy storage systems: sodium-ion batteries and sodium-ion capacitors. The former are hampered by their poor rechargeability due to their low power density, while offering relatively high energy density. The latter, on the other hand, exhibit a high power density, but an extremely low energy density. Therefore, combining capacitor-type cathodes and battery-type anodes in SIHES (sodium-ion hybrid energy storage) cells has been an active area of research, bringing together the best of both worlds.
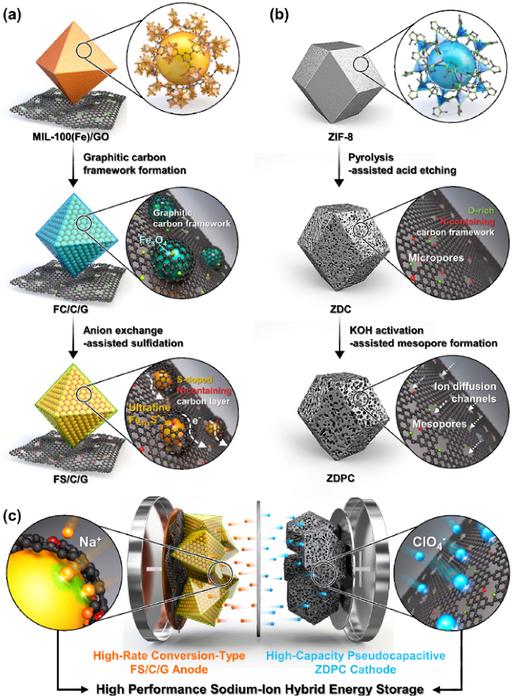
Now KAIST researchers have reported a strategy to realize ultra-high energy density SIHES systems and fast-charging systems. They have used two different metal-organic frameworks for the optimized synthesis of hybrid batteries.
Their approach led to the development of an anode material with improved kinetics through the incorporation of fine active materials into porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks. Furthermore, a high-capacity cathode material was synthesized, and the combination of the cathode and anode materials enabled the development of a SIHES system, optimizing the balance and minimizing the differences in energy storage rates between the electrodes.
The researchers reported that the newly developed hybrid exceeds the energy density of commercial lithium-ion batteries and exhibits the power density characteristics of supercapacitors.
In fact, the SIHES showed an energy density of 247 Wh/kg and a fast-charging power density of 34,748 W/kg, which exceeded the battery-type responses by more than 100 times. It also demonstrated cycle stability with a Coulomb efficiency of approximately 100% over 5,000 charge-discharge cycles.
The KAIST researchers expect broad applications for their new SIHES technology, ranging from electric vehicles to smart electronic devices and space technologies.
They discussed their findings in “Low Crystallinity Conductive Multivalency Iron Sulfide Embedded S-Doped Anode and Large Area O-Doped Cathode of 3D Porous N-rich Graphitic Carbon Frameworks for High-Performance Sodium-ion Hybrid Energy Storage,” which was recently published in Energy storage materials.
This content is copyrighted and may not be reused. If you would like to collaborate with us and reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.