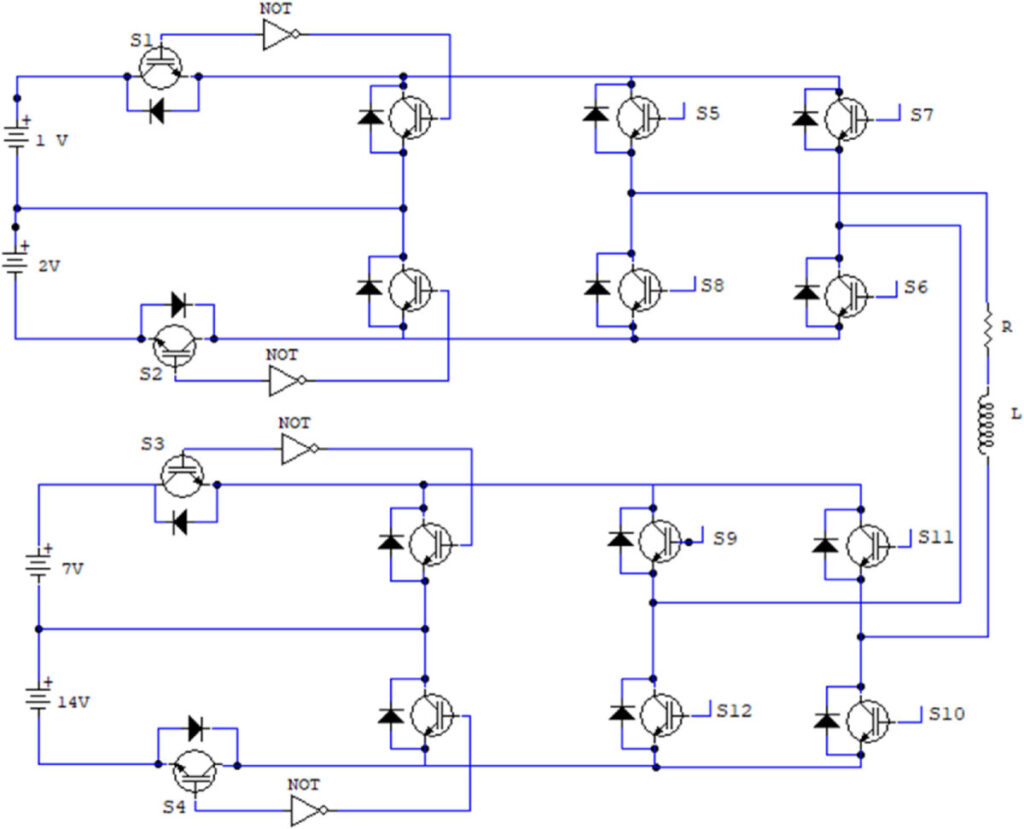
Researchers in Iraq have designed a cascade converter with multiple levels that can produce supposedly of high quality sinus-shaped output voltage and current wave shapes, while reducing harmonic distortion. It uses the so-called phase-Disposition-level pulse width modulation (PDLSPWM) control technology to operate the switches in the circuit “effectively”.
Researchers from Nawroz University in Iraq have designed an asymmetrical cascade converter at 49 level that is said to reduce harmonic distortion and can produce high-quality sinus-shaped tension.
The new Configuration Multi-Level Inverter (MLI) is said to effectively operate the switches in the circuit, thanks to the so-called phase-deposit-level-pulse pulse width modulation (PDLSPWM) control technology for voltage balancing and power scheme.
“The innovative characteristic of this design lies in the ability to reach the starting voltage levels from 3 to 49 with a reduced number of switches, which improves the quality of the power circuit and the overall circuit efficiency is considerably improved,” the scientists explained.
They explained that the PDLSPWM method can reduce the total harmonic distortion (THD) in both the output voltage and the electricity, lower switch losses, in particular in high-voltage applications, and ensure better voltage balancing. “By improving the voltage wave quality and reducing the number of switches, PDLSPWM improves the overall efficiency of the system, making it suitable for both medium and high-voltage applications,” they added.
The research group considered the use of the inverter for a series of simulations in three different scenarios: with DC battery sources configured in a voltage ratio per unit of 1: 7: 14 V; with DC batteries with actual voltage levels of 40: 80: 280: 560 V; where PV replaces the DC sources.
Image: Nawroz University, Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, CC by 4.0
In the first scenario, the scientists said it is suitable for motor drives and renewable energy systems, the inverter turned out to be achieved a wide range of output levels with “improved” wave quality at higher levels, while also the harmonic distortion, power outcome and wave -shape.
With regard to the second scenario, the team discovered that the designed wealth circuit and the controller proven their effectiveness, with the power increasing with rising voltage levels.
In the third case, conceived for project applications such as smart gratings, off-grid systems and integration of renewable energy, the inverter was reportedly able to offer high-quality power with “negligible harmonic” distortion under varying input conditions.
“In case 3, the PV sources give a little worse compared to the other two cases, but the overall results are still within the acceptable range that proves the compatibility of the inverter with green energy -independent systems,” the academics explained. “The proposed MLI with both DC sources and PV sources as input makes it recommended for various applications for renewable energy.”
Their findings are available in the study “Design an asymmetrical 49-level inverter fed by battery and PV energy sources“Published in Case studies in Thermal Engineering.
Looking ahead, the research team is planning to test the proposed MLI design under different charging conditions and controllers.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to work with us and reuse part of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content