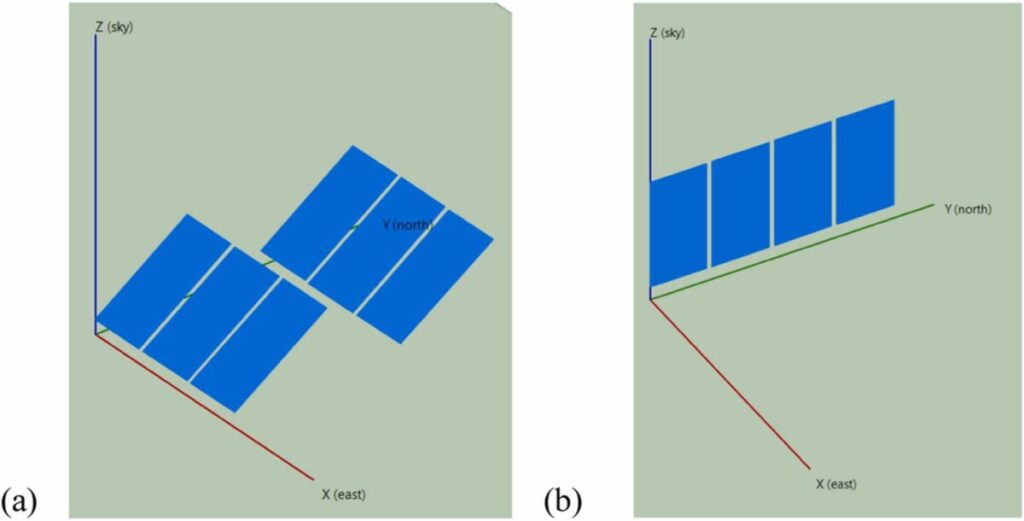
Scientists in Qatar have sketched a new approach to optimize residential bifacial PV systems by combining eastern configurations-oriented and vertically mounted and vertically mounted eastern configurations. The new methodology reportedly results in an increase of 21.6% in the net present value of a system.
A research team led by scientists from Qatar’s University of Doha for science and technology investigated the optimization of bifacial PV panels in a residential setting, aimed at maximizing economic benefits based on charging profiles.
“This research introduces an innovative approach to optimizing bifacial PV panels in residential environments by combining south and east-faced configurations,” said the accompanying author, Muhammad Zubair, PV -Magazine.
With the help of the System Advisory Model (SAM) software, the research team first compared Mono -Facial and Bifacial systems, so that the latter was later optimized under different tax regimes.
“By comparing zero-export-grid-bonds and net measuring configurations, this study offers useful insights into maximizing the net present value (NPV) of PV investments under real-time return conditions,” the scientists said. “In contrast to earlier studies that focus primarily on configurations on the south, this study introduces a hybrid bifacial PV system that is combined to the south of southern and East-West orientations. This innovative approach optimizes Azimuth and tilting angels, which means that three different energy-in-the-day loaders of the whole-speeches” are by the whole-speeches “
The PV systems were simulated on a roof in Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan. The city receives global horizontal irradiation (GHI) of 5.24 kWh/m2/day with an average temperature of 21.3 ° C and an average wind speed of 1.7 m/s. The load of living customers is an average value of 70 houses in the city. Local electricity costs and the costs of different system components were based on different databases. In all cases, the capacity of the system was 5 kW.
The simulation showed that bifacial PV panels produce 10% more energy than a monofacial PV panel placed in the south-facing configuration. Furthermore, it showed that the bifacial panels achieved a 13.6% higher net present value (NPV), a 4.5% lower level of energy (LCOE) and a 5% lower reimbursement period.
By analyzing the height of a vertical bifacial system, with the range of 0 m to 2.5 m, the academics discovered that it had to be placed at least 2 m above the surface. They also noted that a bifacial PV system that is installed at a height of 2 m has a 7.6 times higher NPV than bifacial PV panels that are placed directly on the roof.
Photo: DOH University for Science and Technology, Energy Fields, CC by 4.0
In the case of a zero-export-roster-bound system, which is common in Pakistan, it required the optimized bifacial system for a tilt angle of 30 ° and an azimut corner of 190Z, to produce the highest NPV of $ 2,451 for the customer’s loading profile. If optimizing the system to face the east, the optimum results had to place the panels vertically, which resulted in a 9.7% higher NPV of $ 2,787. However, the last system produced 18.5% lower electrical energy for a year compared to the south -facing.
“These higher economic benefits in producing less energy in vertical bifacial PV systems in the east are due to a longer PV energy generation time compared to a PV panel in the south with a single peak,” the researchers explained. “In the first year, the system in the east was able to fully meet the load for 3,427 hours, while the system in the south was able to satisfy the load for 3,147 hours, which is 8.9% lower than a system in the east.”
A definitive analysis included splitting the system into a 2.5 kW southern unit and a 2.5 kW eastern unit. It showed that the time for which PV energy can be delivered to fully satisfy the load, 4,226ha is years, which is 1,079h more than a Bifacial PV system in the south. The NPV of this system is 21.6% higher than a bifacial PV system on the south of $ 3,091 with an LCOe of 1.87 cents USD/ kWh. The payback time is only 3.43 years, “they thought.
Closing their article, the researchers said that bifacial PV systems must be placed vertically to the east for real-time return network regimes for the availability of electricity in two peaks when other PV plants do not produce on their peak. “The Bifacial PV system in the east offers 362 more H of power generation annually than the Bifacial PV system in the south,” they said.
Their findings appeared in “Optimization of bifacial PV panels in a living sector for maximum economic benefits based on charging profile“Published in Energy reports. Researchers at Qatar’s University of Doha for science and technology and the Pakistani University of Lahore have conducted the study.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to work with us and reuse part of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content