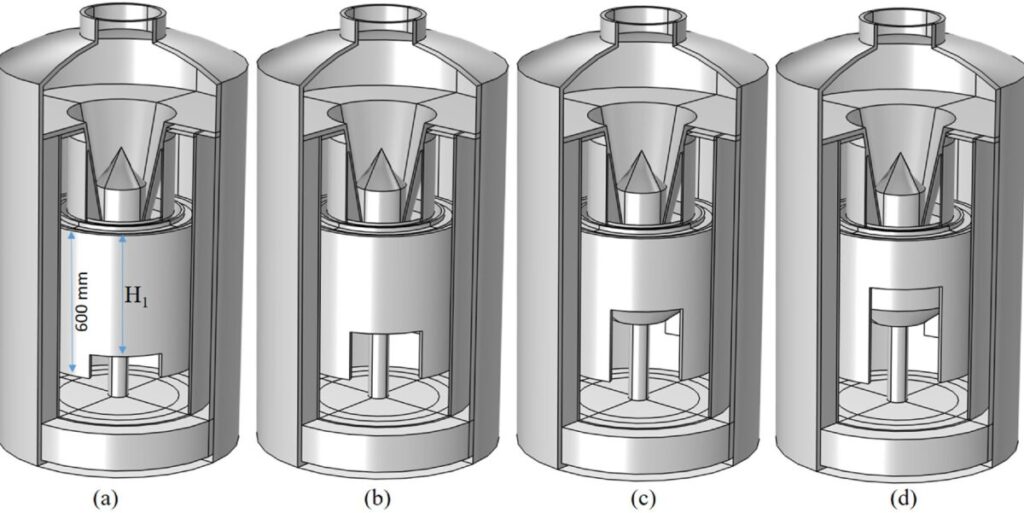
Research from Chin-Yi University of Technology in Taiwan revealed a new heating design in the Czochralski silicon crystal growth process that can control and reduce oxygen concentration without incurring the costs associated with other methods, such as installing magnets or using alternative crucible materials.
Researchers from National Chin-Yi University of Technology in Taiwan have proposed a new heating design for Czochralski silicon crystal growth equipment to control and reduce oxygen concentration.
The method was simulated and validated, finding that the optimal design allowed for an oxygen reduction of 6 parts per million (PPm) atoms.
For both multicrystalline and monocrystalline photovoltaic silicon applications, oxygen is a major impurity problem. For example, it can cause the formation of silicon oxide, which increases the hardness of crystals, which can complicate further processing.
“Our findings indicated that certain oxygen defects shorten the lifetime of the bulk and enhance recombination activity at dislocations,” Amir Reza Ansari Dezfoli, the first author of the study, told me. pv magazine.
There are several ways to tackle these types of problems. “In our research, we focused on controlling, and especially reducing, oxygen impurity by modifying the design of the heater in the Czochralski (CZ) tractor,” Dezfoli said, noting that an oxygen reduction of 6 ppm atoms can be achieved by “simply changing” the design configuration of the heater.
“It was particularly interesting to find that a low-cost adjustment to heating can have a significant impact on oxygen impurity control, demonstrating how a simple adjustment can have a big impact,” he added.
The study first examined heating design and heat source distribution through simulations, and then conducted tests on an experimental setup to validate this. The simulation was based on a CZ crystal growth from a silicon rod with a diameter of 200 mm and a length of 700 mm, with four different heating designs. The heaters were made of graphite and had different top section lengths ranging from 500mm to 200mm.
For validation, a heating height (H1) of 500 mm was used in the experimental setup. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) data analysis was used to measure the oxygen concentrations in the crystals along the axial direction at the rod centerline. Measurements were made of heat transfer and impurity transport, heating power, maximum crystal front deflection and oxygen concentration. Temperature profiles in the heater were analyzed, as well as the impact on the silicon melt and crystals.
The validation comparison confirmed a “strong agreement between simulation and experimental data.”
Concluding that heater design “significantly affects temperature distributions and melting patterns, thereby affecting oxygen distribution and its transport mechanisms,” the article listed the effects of varying the H1 length, noting that it was clear that it controlling the temperature profiles and melt flow patterns was “significant”. affects oxygen distribution.
The group is now preparing to introduce the first discrete model to simulate crystal origin particle (COP) formation and void defect formation during the CZ process. “It will be the first model that can function similarly to laser particle counting in the silicon wafer manufacturing industry, opening new possibilities for simulation-based quality control,” Dezfoli said.
The proposed technology was presented in “Technical insights into the design of heating elements for oxygen reduction in CZ silicon growth”, published in Case studies in thermal engineering,
This content is copyrighted and may not be reused. If you would like to collaborate with us and reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.