Scientists in China have proposed using polydimethylsiloxane films doped with soda glass to reduce the temperature of solar panels. The coating achieved a solar transmittance of 94.8% and a skylight emissivity of 95.3%.
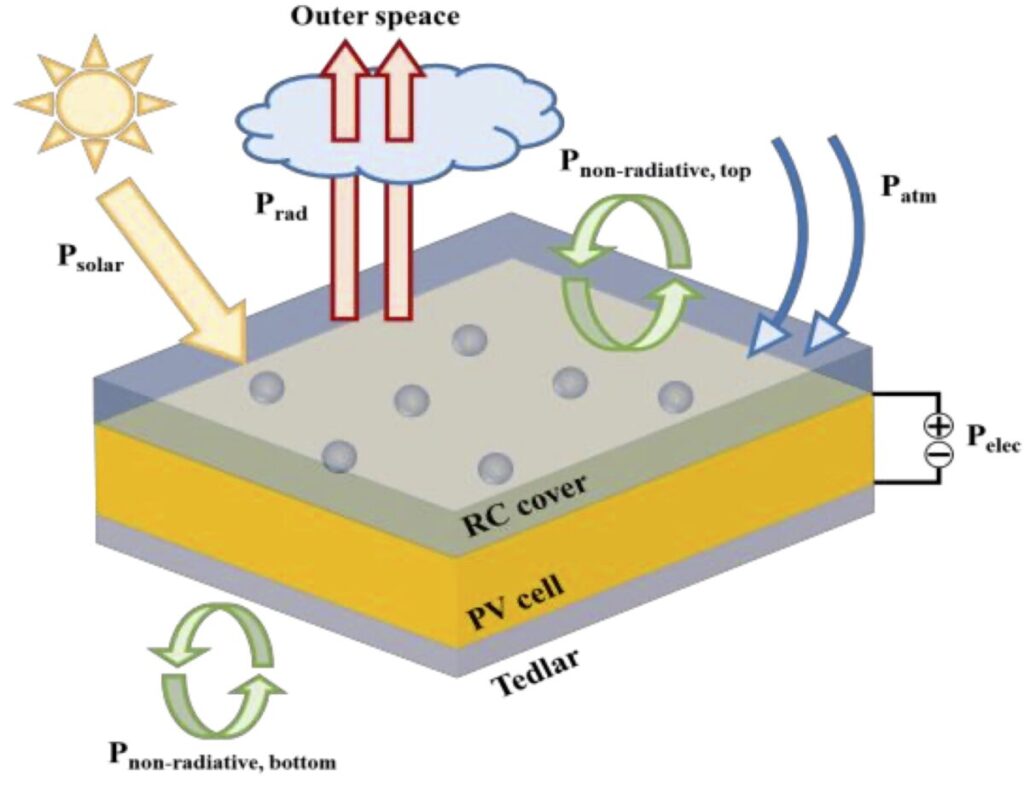
A group of researchers from China’s Shandong University and Xi’an Jiaotong University have developed a radiant cooling (RC) cover for PV panels that can reportedly reduce their operating temperature by up to 3.72%.
Radiative cooling occurs when an object’s surface absorbs less radiation from the atmosphere and emits more. This causes the surface to lose heat and a cooling effect can be achieved without the need for electricity.
“Our study is based on numerical simulations, whose simulation reliability was guaranteed by cross-validations with existing studies, including experimental results,” said corresponding author Dr. Maoquan Huang. PV magazine. “We are also planning experiments to test prototype RC covers on photovoltaic panels under different weather and environmental conditions.”
The new cover is made of polydimethylsiloxane films (PDMS) doped with soda glass (PDMS-SG) and is intended to replace conventional glass covers. “Based on previous studies, this study presents a transparent RC cover with a randomly doped particle structure in a PDMS substrate,” the researchers said. “The study further investigates the efficiency and potential of RC-PV systems in China’s varied meteorological conditions, using hourly weather data.”
Using numerical analysis, the group compared several doping materials, including titanium dioxide (TiO2), tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5), soda glass, silicon dioxide (SiO2), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polystyrene (PS). “Soda glass emerged as the superior choice as it offers an optimal mix of solar transmission and long-wave infrared (LWIR) radiation,” the academics said.
Following this analysis, and also using numerical studies, the group calculated the structural parameters of PDMS-SG that would provide the best radiation results. They found the ideal results when the PDMS-SG film was simulated with a particle diameter of 4 μm, a volume fraction of 1.5%, and a film thickness of 100 μm. This led to a solar transmission of 94.8% and a skylight emissivity of 95.3%, resulting in a peak power of 147.6 W/m2.
After the design optimization, the group simulated the performance in different regions in China. Therefore, the cell was assumed to be a 200 μm thick crystalline Si layer placed above an aluminum (Al) back reflector. It was compared with a reference cell with a 5 mm thick silica glass cover in different regions of China.
“To understand the application potential of RC-PV systems across China, we delineated four different zones based on annual efficiency increases 𝜂,” the group explained. “These zones are named as follows: the optimal application zone (𝜂 ≥ 3.50%), the high potential zone (3.26% ≤ 𝜂 < 3.50%), the medium potential zone (3.02% ≤ 𝜂 < 3.26%) and the limited Potential zone (2.78% ≤ 𝜂 < 3.02%).”
According to their findings, the new RC could increase annual electricity production by 2.78% – 3.72%. The optimal zone of application turned out to be Tibet, as it benefits from a severe cold climate, the most abundant solar radiation and clear skies. Provinces such as Xinjiang were found to be in the high potential zone, while Inner Mongolia was placed in the moderate potential zone. Provinces such as Hunan and Sichuan fell under the limited potential zone of this study.
“The performance of RC PV systems decreased from west to east in China, with the highest increases in regions characterized by dry, cool climates and mostly sunny days,” the academics concluded. “These results highlight the benefits of RC-PV covers under real weather and environmental conditions. This study contributes to the application of RC films to PV systems and provides valuable insights into the use of solar energy in future energy infrastructures.”
Their findings were presented in “The potential of radiant cooling enhanced photovoltaic systems in China,” published in Advances in applied energy.
This content is copyrighted and may not be reused. If you would like to collaborate with us and reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.