Researchers from the Delft University of Technology have developed a top-down processing method to synthesize the localized front contact architecture in solar cells of hetero junction. The new technology is said to make it possible to improve the filling factor and resilience of a cell against breakdown by ultraviolet.
Scientists from Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in the Netherlands have designed a rear junction heterojunction (RJ-SHJ) solar cell with a localized front support-selective passivating contact that only the area covered with the metal schedule.
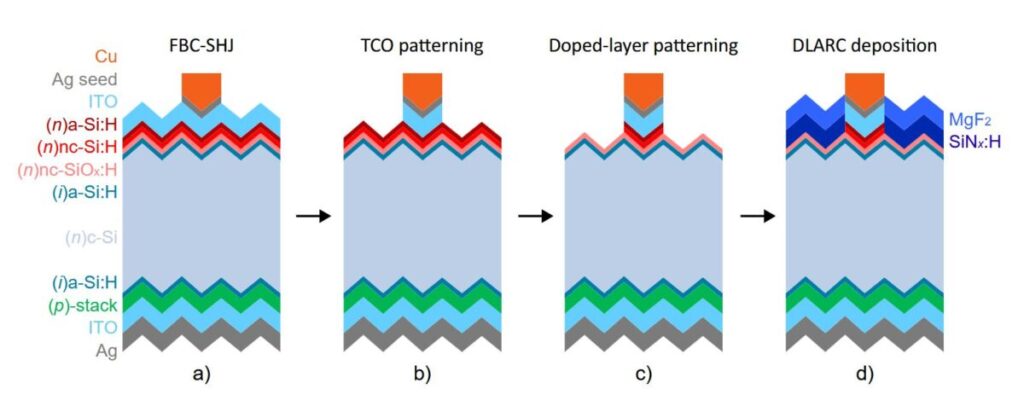
“The most important novelty of our work is the self-released approach to locate the front contact of the cell,” said the main author of the research, Sebastian Smits, said PV -Magazine. “In the past, other research groups have also tried to locate the front contact by omitting the transparent contact oxide (TCO) at the front or locating it by depositing a hard mask. Instead, we have chosen to first fully manufacture a normal SHJ sun cell and then not covered the components of the front.”
The scientists explained that the approach they used to build the localized front contacts does not endanger the mechanical stability of the cells, because it uses metal grid as a mask for local etchings, with the contacts and N-doted layers that are selectively etched from the window openings. ‘By using hydrogenated nanok crystalline silicon (NC-SIOX: H) in the pre-contact, we could do this without resisting losses or damaging the surface passion, which can influence the filling factor and open circuit voltage respectively, “Smits added.
In the next step, the research team introduced a NC-SIOX: H “Stop” layer Between the intrinsic layer and the contact stack, so that the stack of the window openings can be removed full removal of the window openings without affecting the intrinsic layer itself, with an 8 Nm NC-SIOX: H -layer is sufficient to act as a barrier that inhibits the etching of the underlying layer. “In addition to supplying lateral transport of load carriers, the front TCO also acts as an anti-reflecting coating (ARC) that softens the big difference of refractive index between silicon and air,” it emphasized.
The scientists built a 3.96 cm2 with this configuration and discovered that it offers “sufficient” lateral conductivity within the N-type C-Si-Bulk to replace the full front TCO. Tested under standard lighting conditions, the device achieved a power conversion efficiency of 23.4%, an open circuit voltage of 715 mv, a short-circuit current density of 40.5 mA/cm2 and a filling factor of 80.9%.
These results represent the highest values ever registered for a HJT sun cell based on the localized contact architecture for Front.
“Moreover, Van external quantity efficiency (EQE) and spectrophotometry reflection measurements showed the fraction of the light lost due to parasitic light absorption in the localized pre -contact architecture by 1.22 mA cm2 Compared to reference sun cells based on the same precursors, with traditional architecture, “they emphasized.
“The unprecedented preservation of the filling factor in the presented localized pre -contacts opens solar cells for new doors for low contact resistance (N)-Type carrier-selective passivating contacts that make highly efficient front/rear contact (FBC) HJT solar cells that can reduce the indium consumption and improve the resilience against ultraviolet-induced breakdown (UVID), ”they added.
The new concept of solar cells was presented in “Silicone heterojunction solar cells with localized front contacts“Published in RRL Solar.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to work with us and reuse part of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.