In a new weekly update for PV -MagazineSolcast, a DNV company, reports that strong jet stream and eastern storms in April are splitting solar conditions into the US, with the east experiencing a decline in solar radiation, while the northwest saw radiation profits.
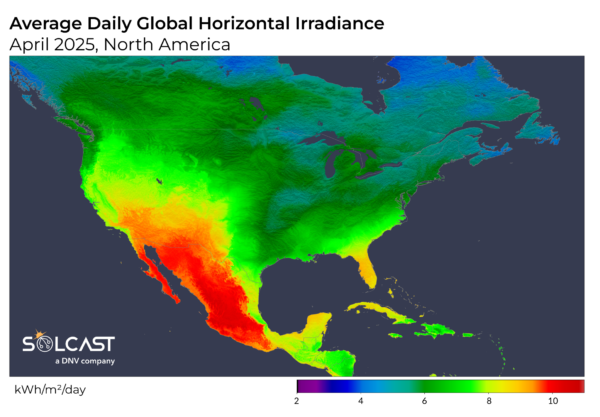
A strong jet stream and eastern storms have splitting solar conditions in the US. According to analysis using the Solcast APISolar conditions were considerably depressed in the eastern US due to persistent storm activity, while the northwest saw clear skies and irradiation in addition to unusually cool temperatures.
In the eastern US, a high -pressure system rode the Atlantic Warm, moist air from the Golf and Atlantic Ocean in the southeast. This humid inflow, trapped between the coast and the Rockies, fed widespread cloud cover and raised rainfall, with temperatures that also ran above average. As a result, the irradiation decreased to 20% below the long -term average April from New England to Oklahoma.
These circumstances were further intensified by a reinforced jet stream that cut the south and inject extra energy into the atmosphere. This setup led to repeated rounds of serious storms and tornado outbreaks, the worsening of the clouds and further reducing the potential for generating solar energy in several regions.
Florida, however, was a remarkable biter. While many of the southeast claimed with persistent cloud covering and storm systems, the state saw relatively dry and sunny conditions. This can be attributed to the position of the high -pressure system. The ridge of higher than normal pressure extended over Florida and promoted more fixed weather. As a result, the State experienced reduced rainfall and clearer skies, which differ sharply from the wetter, cloudy pattern that influences the adjacent States.
The northwestern states, on the other hand, benefited from more stable conditions. A high -pressure system about the Pacific Ocean suppressed cloud formation west of the Rockies, especially in Washington and Oregon. Dry air from Canada contributed to a clearer air and allowed more overnight stay in the absence of blanket clouds. Surface temperatures up to 4 ° C below the long-term average for April were good for efficient performance of solar panels, while the irradiation levels in the northwest by more than 15% rose compared to the long-term average, some favorable conditions for solar operators in the region yielded.
Dissolved Produces these figures by following clouds and aerosols with a resolution of 1-2 km worldwide, with the help of satellite data and own Ai/ml -algorithms. This data is used to stimulate radiation models, so Solcast is able to calculate the radiation at high resolution, with a typical distortion of less than 2%, and also cloud-tracking predictions. This data is used by more than 350 companies that manage more than 300 GW of solar assets worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author, and do not necessarily reflect it by PV -Magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to work with us and reuse part of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content